The VCSA FQDN does not match the certificate in VMware Endpoint Certificate Store Certificate DNS names

Today I was dealing with a vSphere 6.5 environment that was not particularly easy to bring up to 7.0 U3. As soon as I started the update process, the above message went off during the pre-check. Now as you know, even 6.7 U3 is no longer supported, so this update was kind of risky. However, the customer has purchased new servers which could not be added under 6.5 U3, so the environment needs to be updated. Another challenge was that the customer, on the recommendation of another service provider, replaced the vsphere.local domain with a custom domain (no Active Directory, that was additionally integrated).
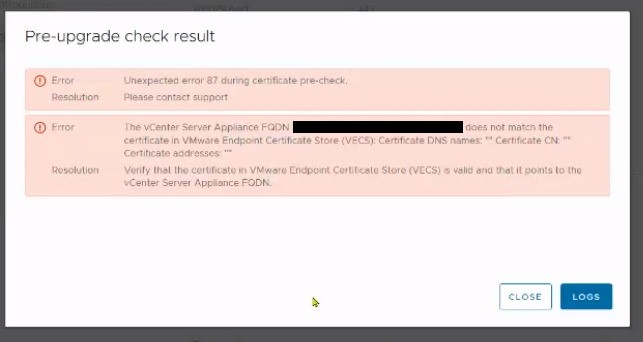
An intermediate update to 6.7 U3 was possible without any problems, but the same warning appeared as soon as I wanted to update to 7.0 U3. Since we still have no support, I had to refer to various KB articles from VMware.
One of the options was to use the vCenter’s built-in certificate manager to generate a new VMCA root certificate to replace them all. The advantage here is that there is a rollback function if the certificate cannot be applied. To do this use the following command:
/usr/lib/vmware-vmca/bin/certificate-manager - OPTION 4
Unfortunately, I do not have detail screenshots, as it is sensitive data. But the generic specifications/reasons for Option 4 are as follows:
- This option can be used when you do not plan on implementing custom CA Certificates signed by either an enterprise CA (like a Microsoft Windows CA) or a Commercial CA (Verisign, GoDaddy, etc.).
- In this environment, the vSphere certificates are generated and issued by the VMCA and stored by the vSphere Endpoint Certificate Store (VECS).
- These certificates are not trusted outside of vSphere by default.
- administrator@vsphere.local password
- Configure the certool.cfg file (used by VMCA when generating certificates)
After entering all the important data and the creation process, the error message was unfortunately still present. I found next possible but also successful solution at lsdoctor.

Lookup Service Doctor (lsdoctor) is a tool used to troubleshoot problems with data stored in the PSC database as well as data local to a vCenter (regardless of whether the PSC is external or embedded). The tool can be used to detect and correct problems that could cause failures during topology changes (converge, repoint, etc.), upgrades, or failures due to maintenance (e.g., incorrect application of new SSL certificates).
To resolve the certificate issue, the lsdoctor – -trustfix command must be run to correct the sslTrust mismatch on the source vCenter Server / Platform Services Controller. To run the lsdoctor, the following steps must be followed:
First download Lsdoctor utility attached to the KB https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/80469. Then copy and extract lsdoctor to the filesystem of any node in the same SSO site as the affected node(s).
Run following command, which depends on your environment:
python lsdoctor.py -t # for regular VCSA
%VMWARE_PYTHON_BIN% lsdoctor.py -t # for Windows vCenter ServerVerify that you have taken the appropriate snapshots. Provide the password for your SSO administrator account and see how the magic works!
After running the lsdoctor with the additional parameter, the certificate problem was solved and the update to vSphere 7.0 U3 could be started without problems and completed successfully.
One last note to my fellow comrades out there in the VMware universe, let’s do something together to help our customers keep their vSphere environments as up to date as possible. That’s about it from this blog post, if you have any questions leave a comment below. 🙂